As more investors look to alternatives to help them reach their investment goals, education is key to success, as is partnering with an experienced investment manager. Use the glossary below to get familiar with the key terms used in the private alternatives space.
Alternatives Glossary
Capital Call
Capital is periodically called down by closed-ended drawdown funds as investments are made; capital calls typically take place during a pre-defined period during a fund’s life (often referred to as the investment period).
Capital Commitment
Amount of capital contractually committed by an investor to the fund that will be called down into the fund over a multi-year time period.
Carried Interest
The General Partner’s share of the profits generated by the fund, which typically range ranges from 10% to 30% depending on the underlying investment strategy. Carried interest is typically earned subject to the fund achieving a certain minimum return (preferred return).
Clawback
Provides Limited Partners the right to recoup a portion of the General Partner’s carried interest where subsequent losses mean the General Partner received excess fees.
Distribution
The disbursement of capital from a fund to an investor.
Equalization
One-time payments that are made to qualified shareholders to compensate for lost dividend income if the dividend schedule of a company is altered.
Extension
When the investment term of a closed-end fund is extended beyond its original length (usually by 1-2 years). This is regularly included as an option for the General Partner to exercise at its discretion with the consent of the Limited Partners.
Fund Level Gate
Provision whereby the fund limits the aggregate amount all investors are permitted to redeem at the prescribed liquidity window, used as a means to slow the pace of redemptions to a rate at which they should have a reduced or limited impact on the value, liquidity, and concentration of a fund’s portfolio.
General Partner (GP)
Fund sponsor/asset manager (i.e., PIMCO); responsible for managing the investments in the fund.
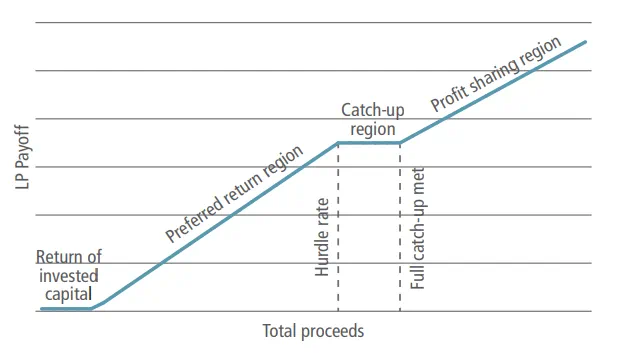
GP Catch Up
After the investor receives their return of called capital and the preferred return, the manager (GP) then “catches up” to receive a portion of the profits splitting subsequent profits in accordance with the pre-specified carried interest structure.
Hard Lock
Liquidity restriction typically found in private funds where the asset manager does not allow redemptions for a pre-defined period of time, typically 1-2 years.
Harvesting Period
Time period after the initial investments have been made and during which the General Partner focuses on managing the investments and exiting them with a goal of distributing capital back to investors. The harvesting period is typically found in drawdown private equity and private debt fund structures.
Hedge Fund
Typically a pooled investment structure set up by an asset manager designed to capitalize on market opportunities to generate positive absolute returns, often through using more complex or sophisticated investment trading strategies.
High Water Mark
The highest peak value that a fund has reached. In the case of a fund featuring a high-water mark, the manager cannot collect fees if the value of the fund is below the high water mark.
Hurdle Rate / Preferred Return
Minimum return threshold a fund must meet before the asset manager can charge an incentive fee or earn carried interest.
Investment Period
Time period during which the General Partner (asset manager) calls and invests capital in investments as part of a closed-end drawdown fund structure. The investment period varies depending on the terms and the investment strategy but typically ranges between 2-4 years.
Investor Level Gate
A provision whereby the fund limits the amount an investor can withdraw from the fund during a particular redemption period.
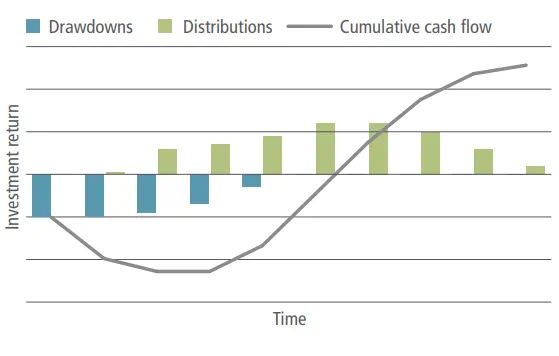
IRR (Internal Rate of Return)
Performance metric most commonly used for private equity style funds, which takes into account the sizing and timing of cash flows (such as capital calls and distributions) and the net asset value at the time of calculation.
J-Curve
Effect whereby closed-end funds tend to experience negative returns in the early years of the fund’s life, which gradually reverses into positive returns over time, resembling a J-shaped profile for an investor’s net cash flows. This occurs because capital commitments take several years to be called, some funds may charge fees on committed capital and other fund expenses may occur (such as deal-related expenses) all while realizations of returns have yet to fully materialize.
Leverage
A strategy of using borrowed capital as a funding source when investing to increase the potential return profile of an investment.
Limited Partner
End fund investor who does not take part in the fund’s management.
Master/Feeder
Fund structure in which investors invest capital into onshore and offshore “feeder” funds, which, in turn, invest assets into a centralized, larger “master” fund, which is managed by the investment manager. This structure is often used to accommodate different categories of investors (e.g. U.S. and non-U.S. investors) and allows for benefits such as economies of scale, reduced trading costs, and tax benefits.
Mezzanine Debt
Subordinated debt that is junior to senior debt. It is capital that is between debt and equity on the right hand side of the balance sheet.
Multiple on Invested Capital (MOIC)
Performance metric often used for private market strategies, which seeks to measure gains on a fund or investment relative to the capital invested.In fund investments, MOIC is expressed as a measure of total value (i.e. both realized and unrealized value) divided by the initial value of the investment.
Offering Period
Time period during which a fund is available for investors to commit to or invest in.
PPM
Private Placement Memorandum is the offering document that outlines the investment opportunity, details risks of investing, and specifies terms and various legal liabilities when investing in a private fund. This document is crucial in making an investment decision.
Private Credit
Debt that is not offered publicly, not filed or registered with any regulatory agency and typically available only to a small subset of large institutional buyers.
Private Equity
Capital, not listed on a public exchange, that is raised to directly invest in private companies, real estate, and usually consists of debt and equity investments.
Private Fund
A pooled investment vehicle that does not solicit capital from the general public, but is instead privately offered to investors.
Private Placement
Securities that are not sold through a public offering, typically offered to a limited pool of investors.
Public Credit
Typically debt that is registered with a regulatory agency and offered publicly. In most cases, public credit (corporate bonds, high yield bonds, etc.) will have a CUSIP/ISIN and is typically liquid.
Repurchase Period
Redemption structure found in interval funds where the fund will repurchase between 5% and 25% of outstanding shares on a quarterly basis.
Soft Lock
Guidelines typically found in private funds where the asset manager imposes a lock on contributions and redemptions but still allows an investor to redeem albeit subject to an early redemption fee. This early redemption fee is typically paid back to the fund.
Subscription Agreement (Sub docs)
An agreement between an asset manager and an investor for the investor to buy and the Fund or partnership to sell a specific number of shares in a private fund at a specific price.
Waterfall
Distribution method that shows the allocation of gains between limited partners and general partners.